org.junit.jupiter
junit-jupiter-api
5.0.0-M3JUnit 5
Next Generation Testing
on the JVM

Nicolai Parlog
Heads Up
JUnit 5 is work in progress!
This is based on Milestone 3
(released 30th of November 2016).
Give feedback!
JUnit 5 Links:
- GitHub repository
- User guide
- Articles on my blog
Tools & Setup
| Tools & Setup |
| Basics |
| Extensions |
Writing Tests
As Easy As Pie!
Add this:
Have fun!
Running Tests
Native support is w.i.p.
Running Tests
As Part Of JUnit 4
individual classes:
@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class) public class JUnit5Test { ... }all classes:
@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class) @SelectPackages({ "my.test.package" }) public class JUnit5TestSuite { }
Running Tests
With Build Tools
JUnit 5 team provides rudimentary
Gradle plugin and Maven Surefire provider
(see user guide for details)
Running Tests
From Console
There is a console launcher:
# run all tests
junit-platform-console \
-cp ${path_to_compiled_test_classes} \
--scan-class-path
# run a specific test
junit-platform-console \
-cp ${path_to_compiled_test_classes} \
--select-class \
${fully_qualified_test_class_name}Tools & Setup
Summary
you can start writing tests right away
only IntelliJ has native support
running with JUnit 4 is a good compromise
(Read about the setup details.)
Basics
| Tools & Setup |
| Basics |
| Extensions |
What’s New?
class JUnit5Test {
@Test
void someTest() {
assertTrue(true);
}
}⇝ Package visibility suffices!
What’s New?
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() { ... }
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() { ... }
@AfterEach
void afterEach() { ... }
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() { ... }⇝ Lifecycle annotations have new names.
What’s New?
@Test
@Disabled("Y U No Pass?!")
void failingTest() {
assertTrue(false);
}⇝ @Ignored is now @Disabled.
What’s New?
@Test
@DisabledOnFriday
void failingTest() {
assertTrue(false);
}⇝ Convenient Extensibility.
But how?
What’s New?
@Test
void someTest() {
...
assertEquals(
expected,
actual,
"Should be equal.");
}⇝ Failure message comes last.
What’s New?
@Test
void someTest() {
...
assertEquals(
expected,
actual,
() -> "Should " + "be " + "equal.");
}⇝ Failure message can be created lazily.
What’s New?
@Test
void assertAllProperties() {
Address ad = new Address(
"City", "Street", "42");
assertAll("address",
() -> assertEquals("C", ad.city),
() -> assertEquals("Str", ad.street),
() -> assertEquals("63", ad.number)
);
}⇝ assertAll gathers results from multiple assertions
What’s New?
Output if assertAll fails:
org.opentest4j.MultipleFailuresError:
address (3 failures)
expected: <C> but was: <City>
expected: <Str> but was: <Street>
expected: <63> but was: (42)What’s New?
void methodUnderTest() {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
@Test
void assertExceptions() {
Exception ex = assertThrows(
Exception.class,
this::methodUnderTest);
assertEquals("Msg", ex.getMessage());
}⇝ assertThrows to assert
exception type and other properties
What’s New?
class CountTest {
// lifecycle and tests
@Nested
class CountGreaterZero {
// lifecycle and tests
@Nested
class CountMuchGreaterZero {
// lifecycle and tests
}
}
}⇝ @Nested to organize tests in inner classes
What’s New?
@DisplayName("A count")
class CountTest {
@Nested
@DisplayName("when greater zero")
class CountGreaterZero {
@Test
@DisplayName("is positive")
void isPositive() { ... }
}
}⇝ @DisplayName to show a nice name
What’s new?
The effects of @Nested and @DisplayName:
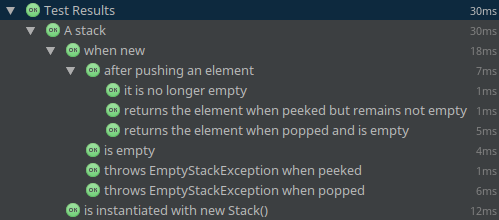
What’s new?
@Test
void someTest(MyServer server) {
// do something with `server`
}⇝ Test has parameters!
But where do they come from?
What’s New?
Summary
lifecycle works much like before
many details were improved
@Nestedand@DisplayName
make a nice coupleparameter injection
no lambdas (so far)
Extensions
| Tools & Setup |
| Basics |
| Extensions |
Extensions in JUnit 4
Runners
Manage a test’s full lifecycle.
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class)
public class MyTest { ... }very flexible
heavyweight
exclusive
Extensions in JUnit 4
Rules
Execute code before and after statements.
public class MyTest {
@Rule
public MockitoRule rule =
MockitoJUnit.rule();
}added in 4.7
lightweight
limited to before/after behavior
Extensions in JUnit 4
Extension model is not optimal:
two competing mechanisms
each with limitations
but with considerable overlap
composition can cause problems
Approach in JUnit 5
From JUnit 5’s Core Principles:
Prefer extension points over features
Quite literally,
JUnit 5 has Extension Points
Extension Points
Test Instance Post Processor
BeforeAll Callback
Test and Container Execution Condition
BeforeEach Callback
Parameter Resolution
Before Test Execution
After Test Execution
Exception Handling
AfterEach Callback
AfterAll Callback
Implementing Extensions
one interface for each extension point
method arguments capture context
public interface BeforeEachCallback
extends Extension {
void beforeEach(
TestExtensionContext context);
}an extension can use multiple points
to implement its feature
Benchmark Extension
We want to benchmark our tests!
for each test method
write the elapsed time to console
How?
before test execution: store test launch time
after test execution: print elapsed time
Benchmark Extension
public class BenchmarkExtension implements
BeforeTestExecutionCallback,
AfterTestExecutionCallback {
private long launchTime;
// ...
}Benchmark Extension
@Override
public void beforeTestExecution(
TestExtensionContext context) {
launchTime = currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override
public void afterTestExecution(
TestExtensionContext context) {
printf("Test '%s' took %d ms.%n",
context.getDisplayName(),
currentTimeMillis() - launchTime);
}Other Examples
Remember This?
@Test
@DisabledOnFriday
void failingTest() {
assertTrue(false);
}Let’s see how it works!
Disabled Extension
public class DisabledOnFridayCondition
implements TestExecutionCondition {
@Override
public ConditionEval.Result evaluate(
TestExtensionCtx. context) {
if (isFriday())
return disabled("Weekend!");
else
return enabled("Fix it!");
}
}Other Examples
What about parameter injection?
@Test
void someTest(MyServer server) {
// do something with `server`
}Parameter Injection
public class MyServerParameterResolver
implements ParameterResolver {
@Override
public boolean supports(
ParameterContext p, ...) {
return MyServer.class
== p.getParameter().getType();
}
@Override
public Object resolve( ... ) {
return new MyServer();
}
}Extension Context
Quick look at ExtensionContext:
// every node has its own context
Optional<ExtensionContext> getParent();
// some node-related info
String getUniqueId();
String getDisplayName();
Set<String> getTags();
// don't use System.out !
void publishReportEntry(
Map<String, String> map);Extension Context
Quick look at ExtensionContext:
// to reflect over the test class/method
Optional<AnnotatedElement> getElement();
Optional<Class<?>> getTestClass();
Optional<Method> getTestMethod();
// use the store to safe extension state
// (extensions should be stateless;
// did I mention that?)
Store getStore();
Store getStore(Namespace namespace);Stateless Extensions
JUnit makes no promises regarding
extension instance lifecycle!
⇝ Extensions must be stateless!
Use the Store, Luke!
namespaced
hierarchical
key-value
Extension Store
Namespaced
Store is accessed via ExtensionContext
given a Namespace
// forwards with a default namespace
Store getStore();
Store getStore(Namespace namespace);keeps extensions from stepping
on each other’s toescould allow deliberate communication!
Extension Store
Hierarchical
Reads from the store forward to other stores:
method store ⇝ class store
nested class store ⇝ surrounding class store
Writes always go to the called store.
Extension Store
Key-Value
The store is essentially a map:
Object getObject(Object key);
Object getOrComputeIfAbsent(
K key, Function creator);
void put(Object key, Object value)
Object remove(Object key)Overloads with type tokens exist.
Stateless Benchmark
void storeNowAsLaunchTime(
ExtensionContext context) {
long now = currentTimeMillis();
context.getStore(NAMESPACE)
.put(KEY, now);
}
long loadLaunchTime(
ExtensionContext context) {
return context.getStore(NAMESPACE)
.get(KEY, long.class);
}Applying Extensions
How do we apply extensions?
@ExtendWith(DisabledOnFridayCondition.class)
class JUnit5Test {
...
}That’s technical and verbose… :(
Applying Extensions
Meta-annotations to the rescue!
JUnit 5’s annotations are meta-annotations
JUnit 5 checks recursively for annotations
⇝ We can create our own annotations!
Creating Annotations
@ExtendWith(DisabledOnFridayCondition.class)
public @interface DisabledOnFriday { }
@Test
@Tag("integration")
@ExtendWith(BenchmarkExtension.class)
@ExtendWith(MyServerParameterResolver.class)
public @interface IntegrationTest { }
@IntegrationTest
@DisabledOnFriday
void testLogin(MyServer server) { ... }Extensions
Summary
flexibility because of many extension points
powerful due to extension context
need to be stateless!
extensions compose well
customizable due to meta-annotations
Questions?
Find Me
Me
you can hire me
since 2016: editor of sitepoint.com/java
2014-2016: Java developer at Disy
2011-2014: Java developer at Fraunhofer ISI
until 2010: CS and Math at TU Dortmund
Image Credits
bubbles: Keith Williamson (CC-BY 2.0)
architecture diagrams:
Nicolai Parlog (CC-BY-NC 4.0)question-mark: Milos Milosevic (CC-BY 2.0)